In-depth analysis of the crocodile leather production process, understanding of the crocodile leather production process, research technology and quality

In-depth analysis of the crocodile leather production process, understanding of the crocodile leather production process, research technology and quality
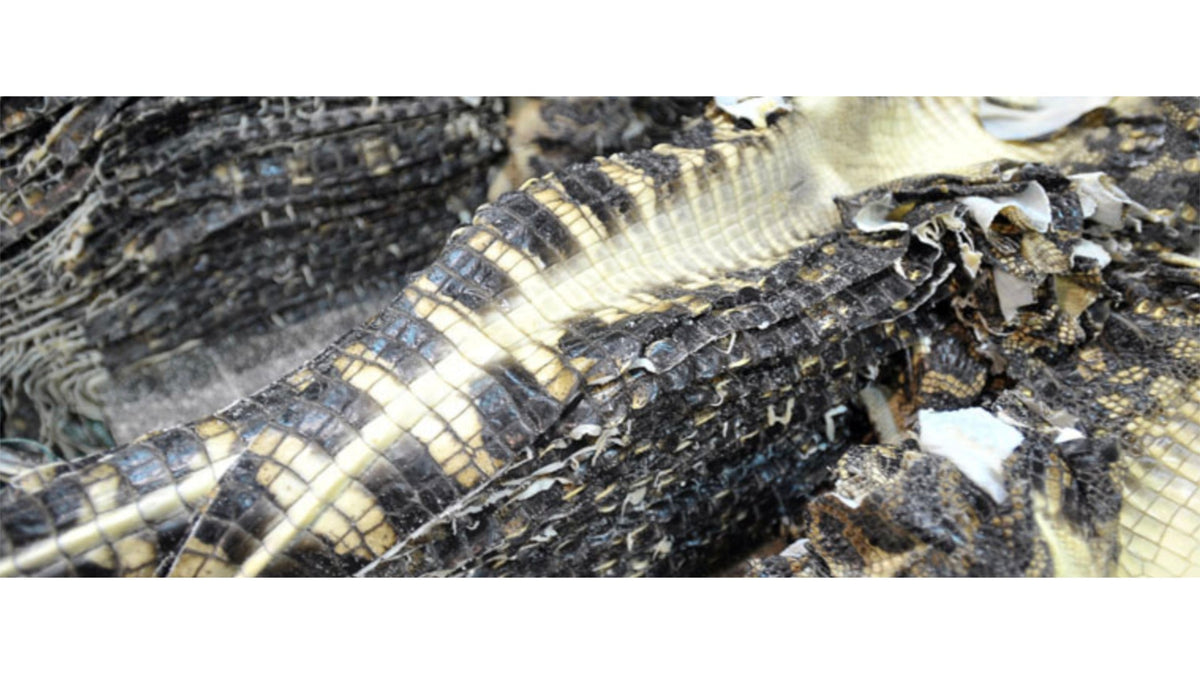
Crocodile leather production process:
- Skinning: Peel off the crocodile skin from the crocodile. The method of skinning crocodile skin is usually to open the belly and leave the belly. A few caiman and Siamese crocodiles use the method of opening the belly and leaving the back. Using this method of opening the belly and leaving the back, The leather retention rate is as high as 90%. With this method of opening the back and leaving the belly, the leather retention rate is only 70%.
- Dry curing: During the curing process, a layer of salt is usually evenly sprinkled on the leather surface to prevent the surface from hardening and to absorb moisture from the leather surface. The type and amount of salt will vary depending on the species of crocodile, the thickness of the leather and the environmental conditions.
- Removing scales: Use a professional skin scraper or sandpaper to remove the scales on the crocodile skin. Because the scale layer of crocodile skin is thicker, if the scales are not removed, it will have a negative impact on the texture and quality of the leather during the tanning process.
- Meat and grease removal: Use a professional skin scraper to soak the leather in a grease-removing solution to remove the grease and flesh fibers from the leather's flesh fibers.
- Salt soaking: Soaking leather in salt water to prevent spoilage and help preserve the leather.
- De-salt: Remove the alligator skin from the brine to remove the salt.
- Thinning: Thin the crocodile leather to about 1.2~1.6mm, making it easier for the solvent to penetrate into the leather fibers in the subsequent process.
- Acidification: When starting to make leather embryos, put the crocodile skin into acid water to lower the pH value. This assists in removing impurities such as fat and protein from the leather, while also promoting the penetration of tanning agents.
- Tanning: Currently it can be mainly divided into two types: vegetable tanning and chrome tanning. Each factory has different tanning formulas.
- Stretching: Also known as stretch leather, clips or nails are used to stretch and fix the crocodile skin. This is mainly to avoid the shrinkage of the leather caused by the tanning process. The shrinkage can be up to 40%, which will also cause damage to the leather surface texture and uneven surface. smooth.
- Dyeing: Also called through dyeing, the alligator skin needs to be soaked in dye first. During the soaking process, the dye penetrates the fiber level of the leather, dyeing the leather to the desired base color. During the dyeing process, attention needs to be paid to the concentration of the dye and the soaking time to ensure the uniformity and depth of dyeing. After dyeing, washing and neutralization are also required to remove excess dyes and chemicals and ensure the dyeing effect and quality of the leather.
- Fixation: Fixation is the process of ensuring the dyeing effect is long-lasting and preventing fading, usually by soaking the leather in a special fixative after dyeing to allow the dye to be better fixed in the leather. The fixation process can also change the effect of the dye, such as enhancing the depth and brightness of the color. .
- Finishing treatment : such as waxing, polishing, oiling, etc. The classic example is that agate stone uses physical methods to polish leather to a shiny surface.
- Crocodile leather finishing: finishing, inspection, grading, packaging
knowledge supplement
- Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of vegetable tanning and chrome tanning for leather
- Remove alligator skin scales
Advantages and Disadvantages of Chrome Tanning :
- High production efficiency, short tanning process time, and capable of mass production
- The leather has good softness, is not easily deformed, is easy to maintain and is durable.
- Leather has high strength and is wear-resistant, water-resistant, and oil-resistant.
- Using synthetic chemical dyes and chemical solvents
- Environmental issues: The chromium tanning process releases harmful chromium ions and other pollutants, causing pollution to the environment.
- Health Risks: Improper practices during the chrome tanning process can expose workers to hazardous substances, posing health risks.
- Quality issues: Improper chrome tanning process may lead to reduced leather quality, such as easy discoloration or breakage.
Advantages and disadvantages of vegetable tanning :
- Environmentally friendly, non-toxic and pollution-free
- The leather feels natural, has clear texture, and has good breathability and moisture absorption properties.
- Leather of different colors, textures and textures can be processed.
- Using natural dyes and natural solvents
- Time-consuming and labor-intensive: The vegetable tanning process is complex and requires a long time and more labor.
- Instability: Vegetable tanning is easily affected by factors such as climate and water quality, resulting in unstable leather quality.
- Waste of resources: Vegetable tanning requires the use of large amounts of water and plant materials, resulting in waste of resources and environmental impact.
Removing crocodile skin scales : The scale layer of crocodile skin is relatively thick. If not removed, it will have a negative impact on the texture and quality of the leather. The scale layer of crocodile skin has a different structure from that of the dermis. Removing the scales can make the texture of the leather more uniform, and there will be no looseness between the scale layer and the dermis layer. In addition, removing scales can make the leather softer and more comfortable to the touch without being too hard. At the same time, removing scales can make the leather surface more uniform, without irregular bulges and lines, and maintain the overall beauty.
1. Dried and salted crocodile hides



2. Lime-soaked crocodile hides

3. Drumming: dry and soft

4. Crocodile Leather Lime Soaked

5.Remove fleshy fibers from leather

6 crocodile leather fleshed fleshing

7.Grading of original crocodile leather

8. Crocodile hides are chrome tanned or vegetable tanned

9. Drying crocodile skin 
10. wet blue grading

11. After the crocodile wet blue leather is completed, it can be stored

12. Crocodile leather wet blue screening and grading

13. Crocodile leather modulation color ratio

14. Crocodile leather dyeing, dyeing base color

15. Crocodile leather color quantity and quality proofreading

16. Crocodile skin drying operation

17. Drying crocodile skin

18. Crocodile leather drying test

19. Crocodile leather records and distribution

20. Crocodile leather hand-painted and colored
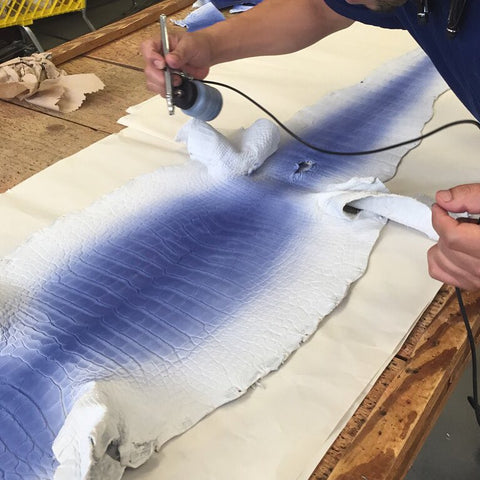

20-1.Hand-rubbed crocodile leather
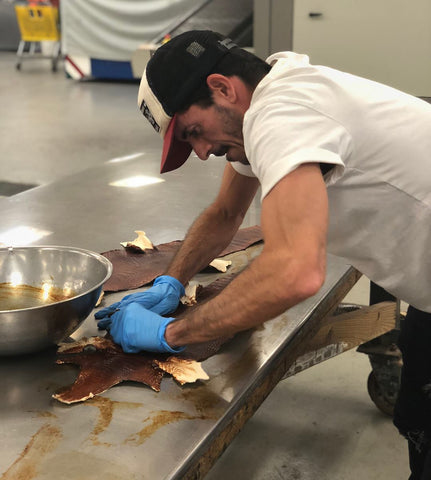

20-2 Crocodile leather multi-layered coloring by hand

20-3 Crocodile leather film metal foil film
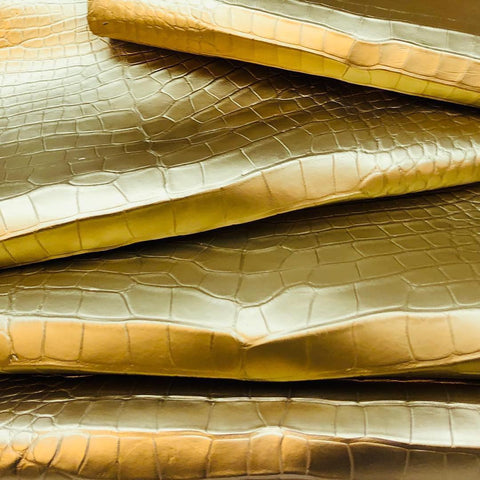

20-5 crocodile leather agate stone polish


20-6 Crocodile leather frosted style roughens the surface of the crocodile leather



20-9 crocodile leather tumbled









Refer to the following information and combine it with your own 30 years of personal experience and resume
"Crocodile: Evolution, Distribution and Conservation" (2002) by Gordon Grigg and David Kirshner: This book is a comprehensive study of crocodiles, including the history of the use and production of crocodile leather.
"The Luxury Strategy: Break the Rules of Marketing to Build Luxury Brands" (2012) by Jean-Noël Kapferer and Vincent Bastien: This book talks about the marketing and branding strategies of luxury goods, including the history and manufacturing process of crocodile leather bags. .
"Handbags: A Love Story: Legendary Designs from Azzedine Alaïa to Yves Saint Laurent" (2015) by Monica Botkier: This book explains the history and development of handbags, including chapters on the making and history of crocodile leather bags.
Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/tanning